Have you ever wondered why you feel down or sluggish, even when everything seems fine? Could a simple nutrient deficiency be the cause? The question “Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?” is more relevant than you might think. Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D plays a crucial role in both our physical health and emotional well-being. A lack of it might be contributing to mood shifts or feelings of sadness, even if you haven’t noticed any obvious signs.
While vitamin D deficiency and depression are separate conditions, emerging research suggests that they might be more connected than we think. Vitamin D impacts brain function and mood regulation, and its shortage could make it harder to feel positive and energised. Understanding this link is essential for anyone experiencing low moods or wondering how their diet might be impacting their mental health.
In this blog post, we will explore the question, “Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?” Whether you’re facing vitamin D deficiency, experiencing low mood, or simply curious about the connection, this article will offer key insights. We’ll dive into the signs of vitamin D deficiency, how it relates to depression, and simple steps you can take to improve both your mood and overall health. And don’t miss the section at the end where we highlight the 10 best supplements for vitamin D deficiency—perfect for jumpstarting your journey to better mental and physical well-being!
Table of Contents
ToggleDeficiency of Vitamin D: What Is It?
Vitamin D deficiency means that your body doesn’t have enough vitamin D, which is an important nutrient for your overall health. Vitamin D is widely known for its role in maintaining strong bones by helping your body absorb calcium. It also supports your muscle function, boosts your immune system, and can affect your mood. You usually get vitamin D from sunlight and certain foods, but if you’re not getting enough sun or not eating enough foods rich in vitamin D, you might become deficient. This deficiency can lead to a variety of health problems, especially those related to bone and muscle health.
The table below provides an overview of the various levels of vitamin D and the associated risk of depression.
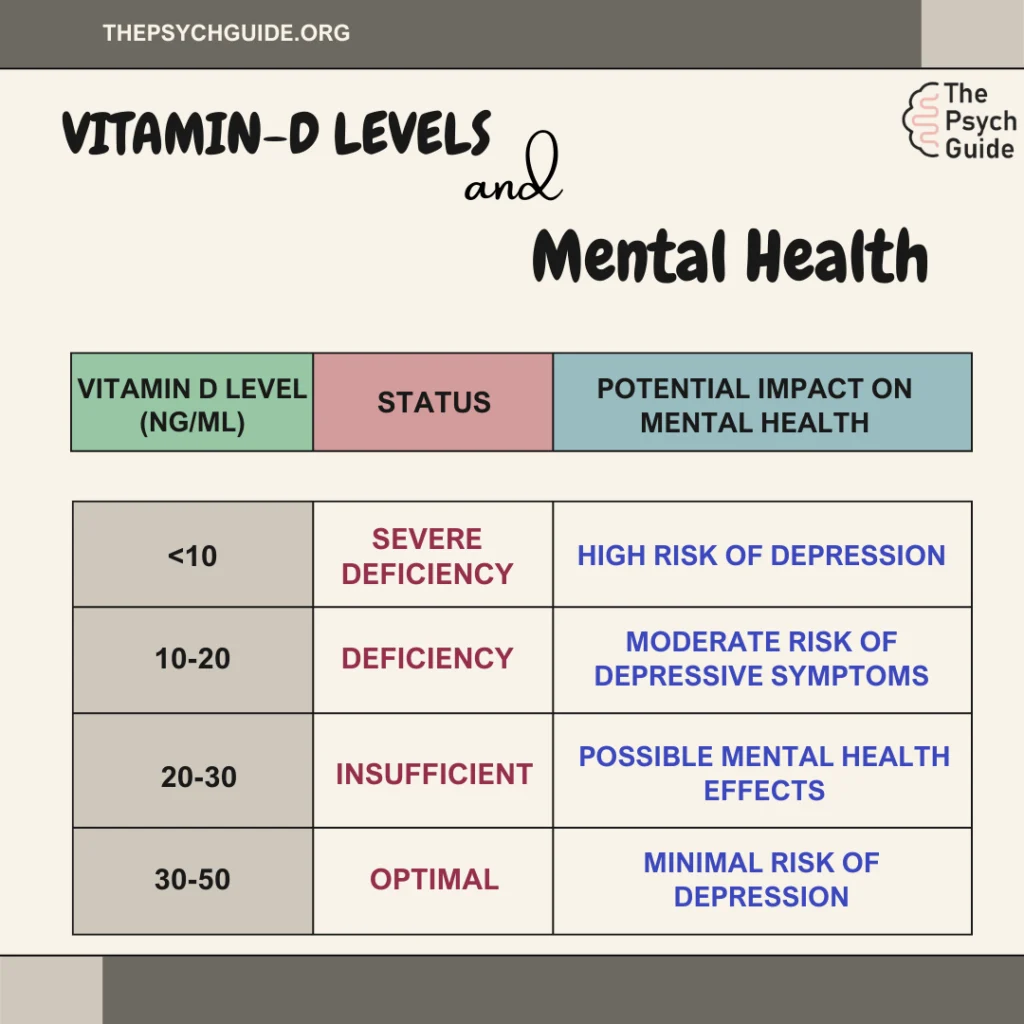
Symptoms Of Vitamin D deficiency
If you are suspecting yourself of lack of vitamin D and depression, then you should look for the following symptoms:
1. Tiredness or Low Energy: One of the most common signs of vitamin D deficiency is feeling unusually tired, even when you’ve had enough rest. Vitamin D helps your body maintain energy levels, so when it’s low, you might feel drained or fatigued.
2. Muscle Weakness or Aches: Without enough vitamin D, your muscles might feel weaker than usual or ache more after regular activities. Vitamin D helps keep muscles strong, so a deficiency can make everyday tasks feel harder.
3. Bone and Joint Pain: Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, which keeps your bones strong. When you’re lacking it, you might feel pain or discomfort in your bones and joints, and over time, this could lead to bigger issues like bone fractures.
4. Feeling Down or Depressed: Low vitamin D levels are linked to mood changes, especially feelings of sadness or depression. The “sunshine vitamin” helps regulate mood, so a deficiency could make it harder to feel positive or motivated.
5. Frequent Illness: Vitamin D plays a key role in keeping your immune system strong. Without enough of it, you might notice you’re catching colds, the flu, or other infections more often than usual.
6. Hair Loss: While hair loss can happen for many reasons, severe vitamin D deficiency may be one of them. It’s rare but possible for low vitamin D levels to affect hair growth and lead to thinning or loss.
7. Slow Healing: If you notice cuts or wounds taking longer to heal, low vitamin D could be a reason. This vitamin helps your body repair itself, so without enough of it, the healing process may slow down.
8. Weak or Brittle Bones: Over time, a vitamin D deficiency can lead to weaker bones, making them more likely to break or fracture. This is because your body needs vitamin D to use calcium effectively and keep your bones strong.
9. Weight Gain: Some research suggests that low vitamin D levels might be linked to weight gain or difficulty losing weight. Vitamin D plays a role in regulating body fat and metabolism, so a deficiency could affect your body’s ability to maintain a healthy weight.
10. Sweaty Head: A lesser-known symptom of vitamin D deficiency is excessive sweating, particularly on the head. If you notice your scalp sweating more than usual without a clear reason, it could be a sign that your body needs more vitamin D.
Vitamin D Deficiency VS Depression
Before answering our question, “Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?”, let’s first compare vitamin D deficiency and depression.
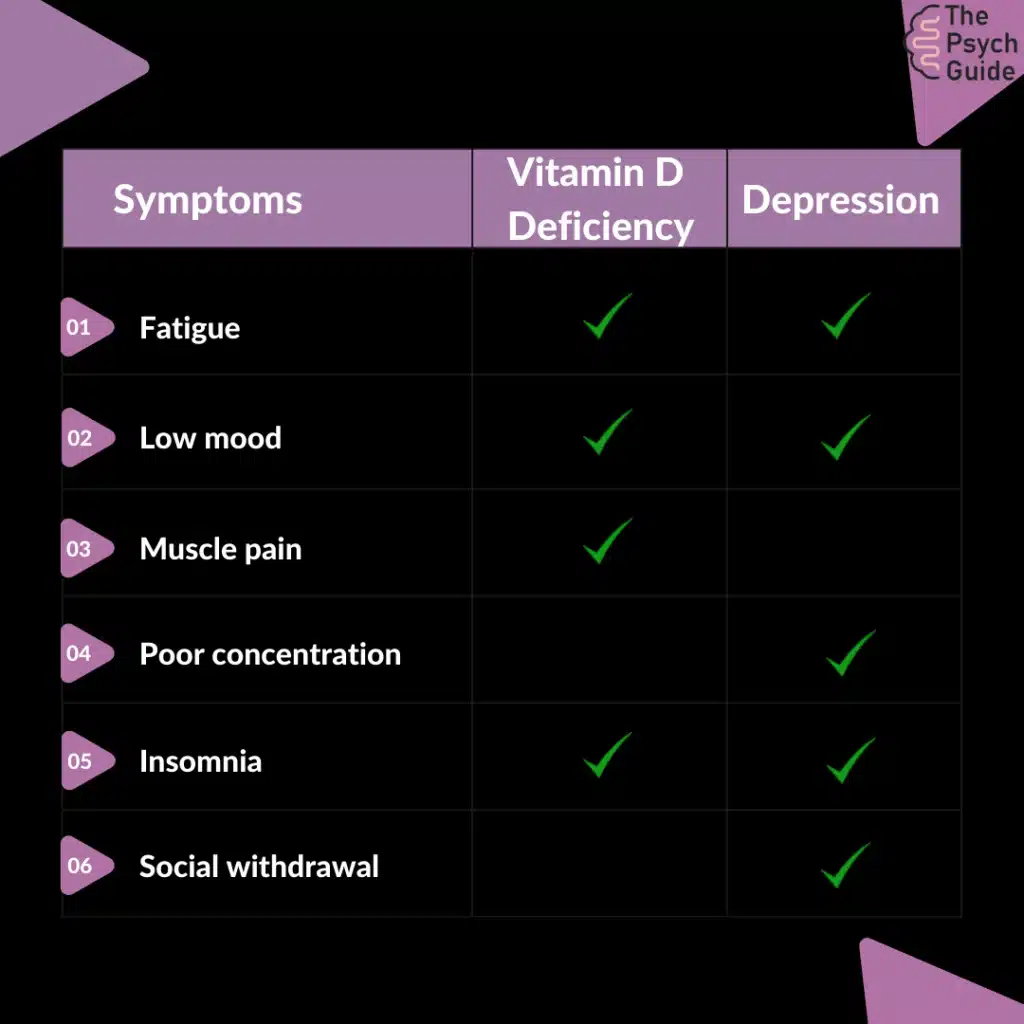
Moving forward to our main topic, “Can Low Vitamin D cause depression” and if yes, then how. Let’s understand this concept in detail.
Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining overall health, but its connection to mental health, particularly depression, has been a topic of increasing interest in recent years. Numerous research studies have explored this connection, providing compelling evidence that low levels of vitamin D can have a significant impact on mood and emotional well-being, linking deficiencies to an increased risk of depression.
The relationship between vitamin D and depression lies in the brain’s use of vitamin D, as receptors for this nutrient are found in areas that regulate mood. When vitamin D levels drop, it can disrupt these brain functions, leading to symptoms like sadness, fatigue, and lack of energy, which are commonly the symptoms of depression.
So, to answer your question, “Can low vitamin D cause depression?” The answer is yes. Vitamin D deficiency can cause depression or contribute to the onset or worsening of depression, making it an important factor to consider in mental health. Now let’s further prove our stance with the help of some research studies.
- In 2015, a study confirmed the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and depression. However, it also suggested that other contributing factors might play a role in this connection.
- By 2017, additional research strengthened the link between vitamin D insufficiency and depression. The study also found evidence that vitamin D supplementation could benefit individuals with clinical depression who are deficient in this nutrient.
- In a longitudinal study from 2021, researchers investigated changes in vitamin D levels and depressive symptoms among older adults. They found that individuals with persistent low vitamin D levels had a higher likelihood of reporting elevated depressive symptoms over time, reinforcing the idea that maintaining adequate vitamin D is crucial for mental health.
- Furthermore, a 2022 follow-up cohort study revealed that individuals with vitamin D deficiency were 75% more likely to develop depression compared to those with adequate levels. This highlights the potential causal relationship between vitamin D deficiency and the onset of depression.
Overall, these studies suggest a strong link between low vitamin D levels and depression, emphasizing the need for further research to establish causality and explore potential treatment options. Now, let’s delve deeper into how vitamin D deficiency can act as a causative factor for depression.
How Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?
Vitamin D deficiency can be linked to various factors that may contribute to feelings of depression. Here are some key elements associated with depression and vitamin d deficiency.
1. Disrupted Serotonin Regulation
Serotonin, known as the “feel-good hormone,” is essential for balancing your mood. Vitamin D plays a key role in the production and regulation of serotonin in the brain. When your vitamin D levels drop, it can reduce serotonin production, leading to feelings of sadness, irritability, and low energy—symptoms commonly associated with depression.
2. Increased Inflammation
Vitamin D helps to fight inflammation in the body, and when you’re deficient, inflammation can rise. Chronic inflammation is linked to depression because it can disturb brain function and chemical balance. Keeping your vitamin D levels in check may help reduce inflammation and its impact on mental health.
3. Impact on the Stress Response System
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis controls how we respond to stress. Vitamin D helps in keeping this system working smoothly. If you’re low on vitamin D, the HPA axis can become disrupted, leading to an exaggerated stress response, which can make you more susceptible to mood disorders like depression.
4. Low Energy Levels
Optimum Vitamin D levels keep you energetic but when you have a deficiency, it can cause fatigue, leaving you feeling drained, unmotivated and hopeless. These are common feelings that go hand-in-hand with depression.
5. Altered Dopamine Function
Dopamine is the brain’s “motivation” neurotransmitter, influencing how we feel pleasure and stay motivated. Vitamin D helps regulate dopamine levels, so a deficiency can result in lower dopamine activity. This can lead to feelings of sadness, lack of interest, and even an inability to enjoy things which are key symptoms of depression.
6. Sleep Problems
Vitamin D also plays a role in regulating sleep. When you’re deficient, it can interfere with your sleep patterns, causing insomnia or poor-quality sleep. Since good sleep is essential for emotional stability, poor sleep can worsen symptoms of depression.
7. Weakened Immune System
A strong immune system is essential for both physical and mental health. Vitamin D supports immune function, and a deficiency can leave you more susceptible to illness. This can increase stress and further contribute to feelings of depression.
By understanding these processes, it’s clear that a lack of vitamin D can significantly influence the development or worsening of depression. Identifying and correcting this deficiency can be a key step in improving mental well-being.
Now, let’s dive into what causes vitamin D deficiency.
Causes Of Vitamin D Deficiency
The following are some of the causes of vitamin D deficiency:
- Limited Sun Exposure: Reduced time spent outdoors, especially in colder climates, decreases natural vitamin D synthesis.
- Living in Northern Latitudes: People living far from the equator get less UV light, especially in winter, limiting vitamin D production.
- Sunscreen Use: Regular use of sunscreen blocks UV rays, which are needed for the skin to produce vitamin D.
- Darker Skin Pigmentation: Higher levels of melanin in darker skin reduce the skin’s ability to synthesise vitamin D from sunlight.
- Indoor Lifestyles: Spending the majority of time indoors for work or leisure reduces sunlight exposure and vitamin D production.
- Pollution: Air pollution can block UV rays, preventing them from reaching the skin and reducing vitamin D synthesis.
- Dietary Deficiency: A lack of vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy, and eggs can lead to deficiency.
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys play a crucial role in converting vitamin D into its active form, and kidney dysfunction can impair this process.
- Liver Disease: The liver is also involved in processing vitamin D, and any liver impairment can contribute to deficiency.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can sequester vitamin D, making it less available for use in the body.
- Bariatric Surgery: Surgical procedures like gastric bypass can reduce the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D due to alterations in the digestive system.
- Ageing: Older adults have thinner skin and less efficient vitamin D production, along with potential reduced sun exposure.
- Breastfeeding without Supplementation: Breast milk alone may not provide sufficient vitamin D for infants unless the mother has adequate levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids or anticonvulsants, can interfere with vitamin D metabolism in the body.
- Genetic Factors: Some people have genetic variations that make it harder for their bodies to produce or use vitamin D effectively.
- Chronic Illnesses: Chronic illnesses, especially those that limit mobility or outdoor activity, can indirectly reduce sunlight exposure and vitamin D levels.
How to Overcome Vitamin D Induced Depression?
The following treatments can help to overcome vitamin d induced depression:
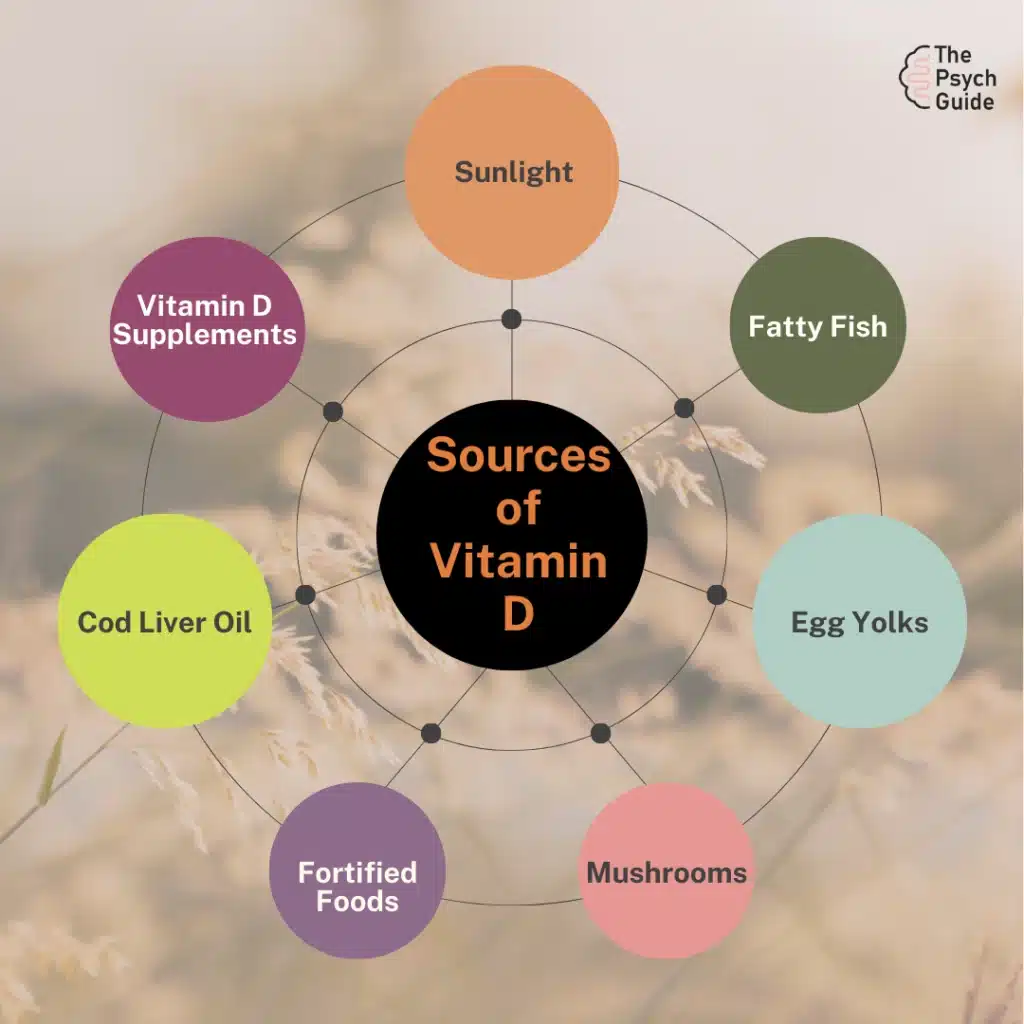
1. Sunlight Exposure
Regular sunlight exposure is crucial for the natural production of vitamin D, which is essential for mental health and mood regulation.
- How it works: Sunlight stimulates the skin to produce vitamin D, which plays a role in serotonin production, a neurotransmitter linked to mood.
- Effectiveness: Especially beneficial for those with seasonal affective disorder (SAD), improving mood and reducing depressive symptoms during the winter months.
2. Dietary Adjustments
Incorporating vitamin D-rich foods into your diet can help elevate your levels of this crucial nutrient.
- How it works: Foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks provide direct sources of vitamin D.
- Effectiveness: This approach is beneficial for individuals who may not get adequate sunlight or prefer a specific diet, helping alleviate symptoms associated with vitamin D deficiency.
3. Vitamin D Supplements
Taking vitamin D supplements is a straightforward way to address deficiencies, particularly in individuals with limited sun exposure or dietary intake.
- How it works: Supplements provide a concentrated source of vitamin D, enhancing levels in the body quickly.
- Effectiveness: Research shows that supplementation can significantly improve mood and reduce depressive symptoms in those diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency.
4. Light Therapy
Light therapy involves exposure to bright light that mimics natural sunlight, commonly used to treat depression and seasonal affective disorder.
- How it works: The light from therapy boxes triggers biochemical changes in the brain similar to those produced by sunlight, increasing serotonin levels.
- Effectiveness: Effective for many individuals living in cold areas with SAD or low vitamin D, leading to improvements in mood and energy.
5. Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can enhance vitamin D levels and improve mental health.
- How it works: Exercise boosts overall health and encourages the body to produce vitamin D naturally, especially when done outdoors.
- Effectiveness: Exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, providing a dual benefit alongside vitamin D production.
6. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a structured therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours.
- How it works: By addressing the cognitive aspects of depression, CBT can lead to improved coping mechanisms and emotional resilience.
- Effectiveness: Studies have indicated that combining CBT with vitamin D supplementation can enhance overall treatment outcomes for depression.
7. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress and promote mental well-being.
- How it works: These techniques reduce cortisol levels, allowing the body to utilise vitamin D more effectively and improve mood stability.
- Effectiveness: Regular practice can significantly alleviate symptoms of depression, contributing to a better quality of life.
8. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Increasing intake of omega-3 fatty acids through diet or supplements can complement vitamin D’s effects on mental health.
- How it works: Omega-3s support brain health and can enhance the effectiveness of vitamin D in regulating mood.
- Effectiveness: Research suggests that combining omega-3s with vitamin D supplementation may improve symptoms of depression more effectively than either alone.
9. Hormonal Balancing
For some individuals, hormonal imbalances may contribute to depression, and addressing these can aid in recovery.
- How it works: Treatments may involve hormone replacement therapy or lifestyle changes that stabilise hormonal levels, including vitamin D’s role in hormonal health.
- Effectiveness: Proper hormonal balance can significantly improve mood and decrease depressive symptoms, particularly in women experiencing menopause or thyroid issues.
10. Regular Health Check-ups
Regular visits to healthcare professionals can help monitor vitamin D levels and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- How it works: Health check-ups can include blood tests to assess vitamin D levels and overall health, allowing for timely interventions.
- Effectiveness: Keeping track of vitamin D levels can lead to more effective management of depressive symptoms and ensure comprehensive care.
10 Best Vitamin D Supplements
The following are the most useful and one of the best sellers supplements available for vitamin D deficiency worldwide:
NatureWise Vitamin D3 5000 IU (125 mcg)

- 5000 IU of vitamin D3 per mini softgel.
- Non-GMO and gluten-free.
- Unflavored
- Compact, easy-to-swallow softgels.
Nature Made Vitamin D3 2000 IU (50 mcg)

- 2000 IU (50 mcg) of vitamin D3 per softgel.
- No color added and unflavored.
- Suitable for vegetarians
- 100 tablets per bottle for daily use.
NOW Foods Supplements, Vitamin D-3 5000 IU

- 5000 IU of vitamin D3 per softgel.
- Non-GMO, gluten-free, soy-free, and low sodium.
- Halal, Kosher, corn-free, dairy-free, and egg-free.
- Highly absorbable liquid softgel, unflavored.
Nature Made Vitamin D3 K2, 5000 IU

- 5000 IU of Vitamin D3 + 100 mcg of Vitamin K2 per softgel.
- K2 helps direct calcium to bones.
- No synthetic dyes or artificial flavors; unflavored.
- Convenient two-pack for continued use.
- High-quality ingredients with gluten-free
Vitafusion Vitamin D3 Gummy Vitamins

- 50 mcg (2,000 IU) of vitamin D3 per serving.
- Natural fruit flavors with a satisfying chewy texture.
- No gluten, dairy, high-fructose corn syrup, artificial sweeteners, or synthetic dyes.
- Perfect for those who prefer gummies over pills.
- 150 gummies per bottle, lasting 75 days.
Metagenics Vitamin D3 + K

- 125 mcg (5,000 IU) of vitamin D3 per softgel.
- Includes bioavailable vitamin K2 for enhanced support.
- Gluten-free, non-GMO, and unflavored.
- Manufactured by Metagenics, trusted by doctors.
- Quality Assurance: Covered by Metagenics 60-day satisfaction guarantee.
Organic Vitamin D3 K2 Drops w MCT Oil Omega 3

- 5000 IU (125 mcg) of Vitamin D3, 120 mcg of Vitamin K2, and 250 mg of Omega 3 per serving.
- Liquid form for quicker absorption compared to capsules.
- Non-GMO, filler-free, and USA-made.
- Available in unflavored, mocha, pineapple, strawberry, and vanilla.
- 2 Fl Oz per bottle (Pack of 2).
- Hassle-free refund or replacement policy.
Dr. Berg D3 K2 Vitamin

- 10,000 IU of Vitamin D3 and 100 mcg of Vitamin K2.
- Includes Vitamin B6, Zinc, Magnesium, MCT, and OxBile for better absorption.
- Sourced from high-quality, domestic and international farms.
- Suitable for keto diets. No added flavor.
- 120 capsules per bottle for a 120-day supply.
- 30-day refund guarantee if not satisfied.
Bronson Vitamin K2 (MK7) with D3

- 5000 IU of Vitamin D3 and 90 mcg of Vitamin K2 (MK7) per capsule.
- Non-GMO, gluten-free, and soy-free.
- 120 easy-to-swallow capsules per bottle.
- No added flavor.
THORNE Vitamin D-5000

- 5000 IU of vitamin D3 per capsule.
- NSF Certified for Sport, ideal for high-performance nutrition programs.
- Chosen by champions and trusted by over 100 pro teams.
- Free from gluten, eggs, tree nuts, peanuts, dairy, soy, fish, and shellfish
- Gluten-free and unflavored 60 capsules per bottle
Note
The amount of vitamin D a person needs can vary based on age, health, and whether they have a deficiency. It’s always best to consult your doctor before starting a vitamin D supplement, especially if you have a health condition or are pregnant. Taking too much vitamin D can be harmful.
Here’s a simple breakdown for daily vitamin D intake:
- For Vitamin D Deficiency: If you are deficient, your doctor might recommend a higher dose to boost your levels. Common doses are 1000–5000 IU (25–125 mcg) per day, but it’s crucial to consult a doctor before starting any high-dose supplements.
- For Normal Vitamin D Levels: If your levels are already in the normal range, a daily intake of 600–2000 IU (15–50 mcg) is generally sufficient to maintain healthy vitamin D levels and support bone and immune health.
Conclusion
Lastly, the question “Can Low Vitamin D Cause Depression?” has already been discussed. And it’s clear that low levels of vitamin D can have a significant impact on mental health, potentially contributing to depressive symptoms. While vitamin D alone may not be the sole cause of depression, maintaining adequate levels is important for overall well-being. Ensuring sufficient vitamin D intake can play a vital role in supporting mood and reducing the risk of depression.
Frequently Asked Questions
These are some of the frequently asked questions in addition to the main query, “ Can Vitamin D deficiency cause depression?”.
- What is the relationship between vitamin D and seasonal affective disorder?
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating mood, and a lack of vitamin D is often linked to seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression that occurs at specific times of the year, usually during winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
In June, a study confirmed that B vitamins, vitamin C, and vitamin D may help prevent and treat depression and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), though more research is needed to understand their mechanisms and optimise treatment strategies.
- Can vitamin D help with depression?
Yes, studies suggest that adequate levels of vitamin D can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Supplementing with vitamin D may be particularly beneficial for individuals who are deficient in this vitamin.
According to a 2011 study, vitamin D deficiency is common in individuals with depression and treating it may be a cost-effective way to improve mental health and quality of life.
- How is vitamin D for depression effective?
Vitamin D supports the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation. Ensuring sufficient vitamin D levels can therefore be an important factor in managing and preventing depression.
- How does vitamin D deficiency cause depression?
A lack of vitamin D can disrupt neurotransmitter function and hormone levels, which can contribute to feelings of depression. Low vitamin D levels are associated with increased risk for mood disorders, including depression.
- What are the symptoms of low vitamin D and depression?
Common symptoms include fatigue as both low vitamin D and depression makes you tired, irritability, mood swings, and an overall sense of hopelessness. Individuals may also experience physical symptoms such as muscle weakness and pain.Individuals experiencing persistent feelings of sadness or lethargy may benefit from testing their vitamin D levels.
- How can I increase my vitamin D levels to improve my mood?
To increase vitamin D levels, consider getting more sunlight exposure, eating vitamin D-rich foods (such as fatty fish, fortified dairy, and egg yolks), and taking vitamin D supplements if necessary.
- Can vitamin D supplements help reduce symptoms of depression?
Yes, vitamin D supplements can help alleviate symptoms of depression, especially in individuals with diagnosed deficiencies. Regular monitoring and dosage adjustment are recommended for optimal results.
According to a study, low vitamin D levels are linked to depression, with evidence suggesting that vitamin D supplementation may have a stronger therapeutic effect in individuals with major depression and concurrent vitamin D deficiency.
- Can Depression cause low vitamin d levels?
Depression can contribute to vitamin D deficiency through several mechanisms. Individuals with depression may spend less time outdoors, leading to reduced exposure to sunlight, which is necessary for the body to produce vitamin D. Additionally, depression can result in poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and neglect of health, all of which can decrease vitamin D intake and absorption. Hence it results in low vitamin D and depression.Furthermore, some studies suggest that depression may alter the body’s metabolism of vitamin D, making it less effective.
According to a study from 2022, individuals with depression in Peshawar, Pakistan, had a higher prevalence of vitamin D deficiency compared to healthy subjects. It observed that vitamin D deficiency was more common in females and that mild deficiency was associated with depression.
- Are there any risks associated with vitamin D supplementation?
While vitamin D is generally safe, excessive intake can lead to toxicity. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation to determine the appropriate dosage.
Earlier in January, a study suggested that vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced depressive symptoms in adults with primary depression and serum 25(OH)D levels higher than 50 nmol/L.
- Can lifestyle changes affect vitamin D levels and overall mental health?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as increased outdoor activity, dietary modifications, and stress management techniques can fix lack of vitamin D and depression as it enhances vitamin D levels and contribute positively to mental health and overall well-being.

